Outline ¶
- EEG signals and brainwaves
- Event-related potential (ERP) signals
and mismatch negativity (MMN) - Predictive coding
- The HBP-Canon project
- Summary
EEG signals and brainwaves
Electroencephalography (EEG) ¶
- Monitoring brain activity via
electric potential - Change in ionic currents (Na, K, Ca)
- Non-invasive or invasive
(electrocorticography) - Main purposes: epilepsy,
sleeping disorders, depth of anaesthesia - Evoked potentials (EP),
event-related potentials (ERP)
Brainwaves
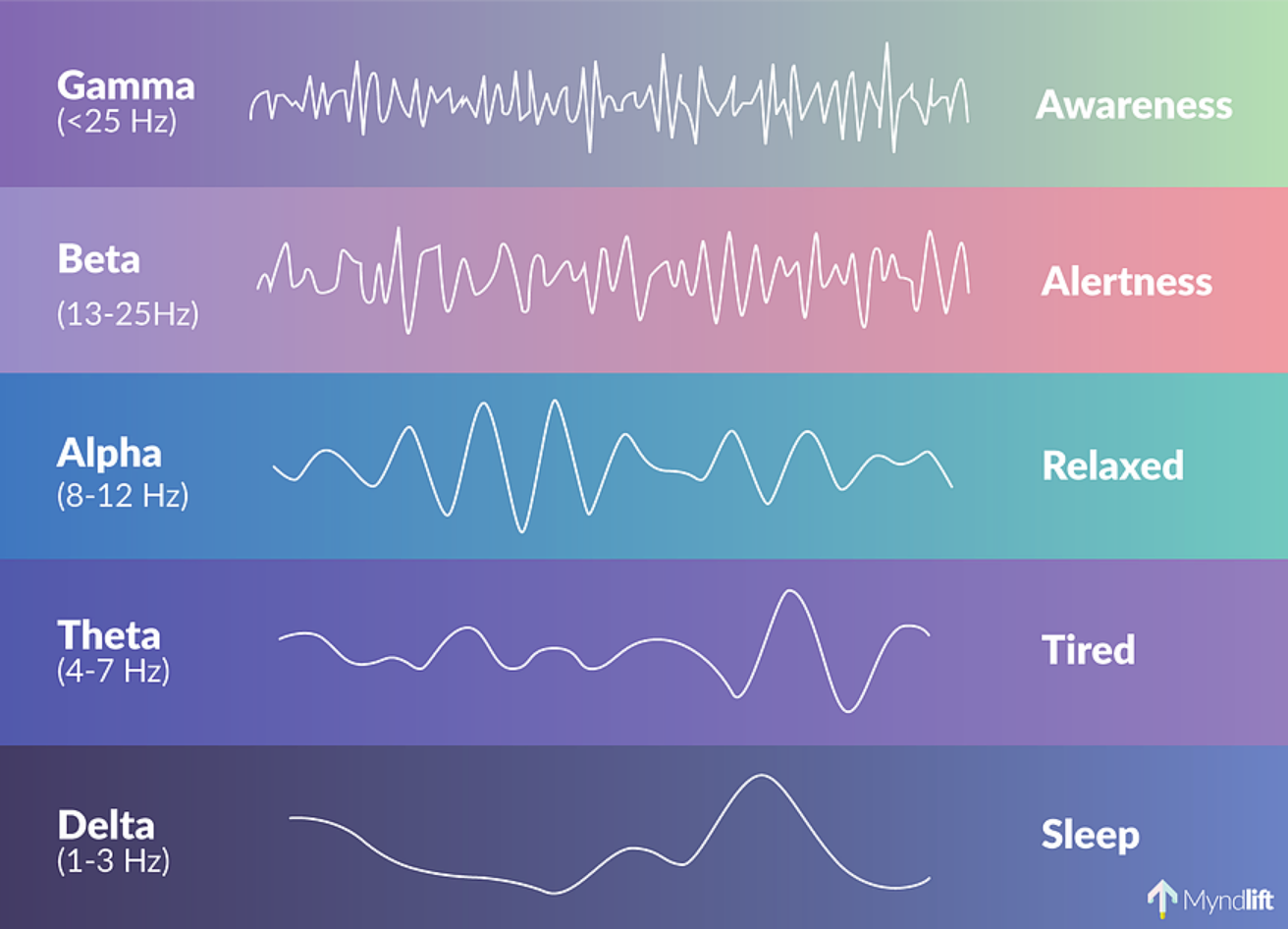
- Rhytmic neural oscillations
generated by the neaural tissue - First discovered in 1924 by Berger
- Characterized by the frequency,
amplitude and phase - Output is the mixture of all
- Phase synchrony
ERP & MMN
Event-related potentials (ERP) ¶
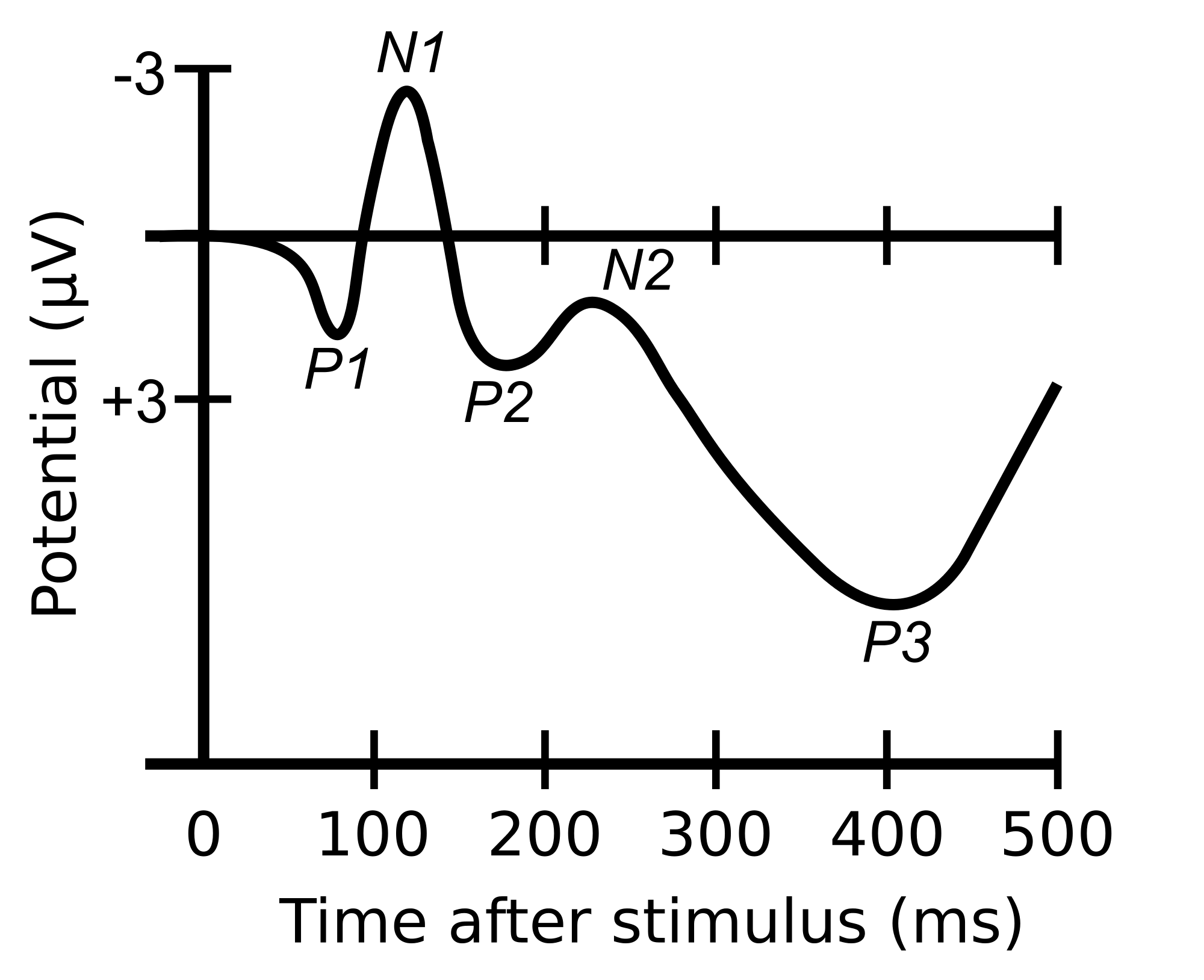
- Result of sensory, cognitive or motory event
- Needs many trials and averaging $$ {\bar x}(t)={\frac {1}{N}}\sum _{{k=1}}^{N}x(t,k)=s(t)+{\frac {1}{N}}\sum _{{k=1}}^{N}n(t,k) $$
- P300 = Positve peak after 300 ms AS
- Fields of occurrence include:
- AD/HD
- Parkinson's disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- etc.
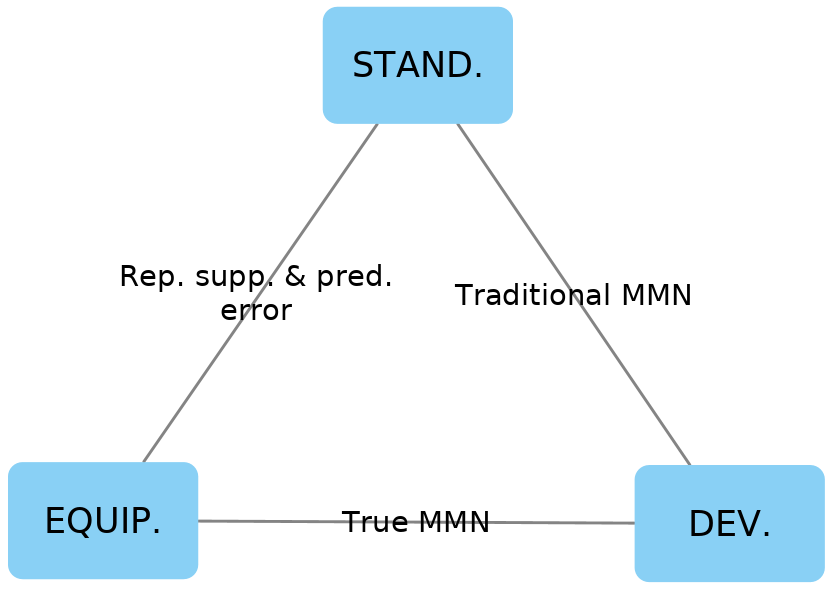
Mismatch negativity (MMN) ¶
- Component of ERP
Standard and deviant stimuli
[s s s s s s s s s d s s s s s s d s s s d s s s s...]
Common base is the representation of our world
- Memory trace or no memory neurons
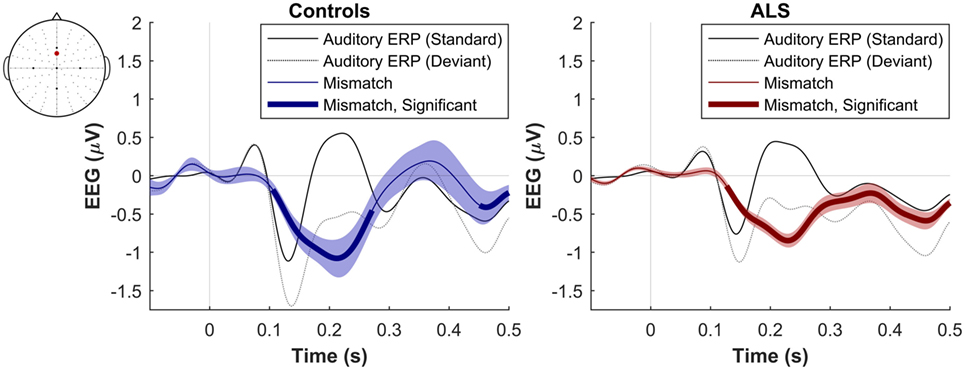
Predictive coding ¶
- Brain generates hypotheses about the future
- Repetition suppression (RS): reduction of neural response
- Surprise enhancement (SE): prediction error
- Ratio of the RS and SE
- Equiprobable series
Short summary
What we know ¶
- Brainwaves by the frequency
- Mismatch negativity
- Repetiton suppression and prediction error
- Standard, deviant and equiprobable series
The HBP-Canon project ¶

- Swammerdam Institute for Life Sciences,
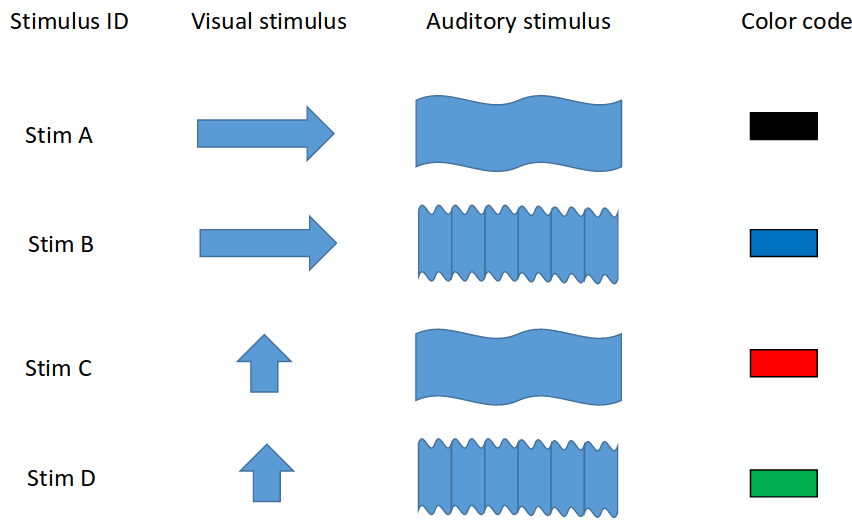
University of Amsterdam - Rats and mice, auditory and visual
stimuli (4 types) - Measured in auditory and visual
corteces invasively (AL, V1) - 2 x 32 channels, 32 kHz sampling frequency
- Appr. 500 GB of raw recordings
Results ¶
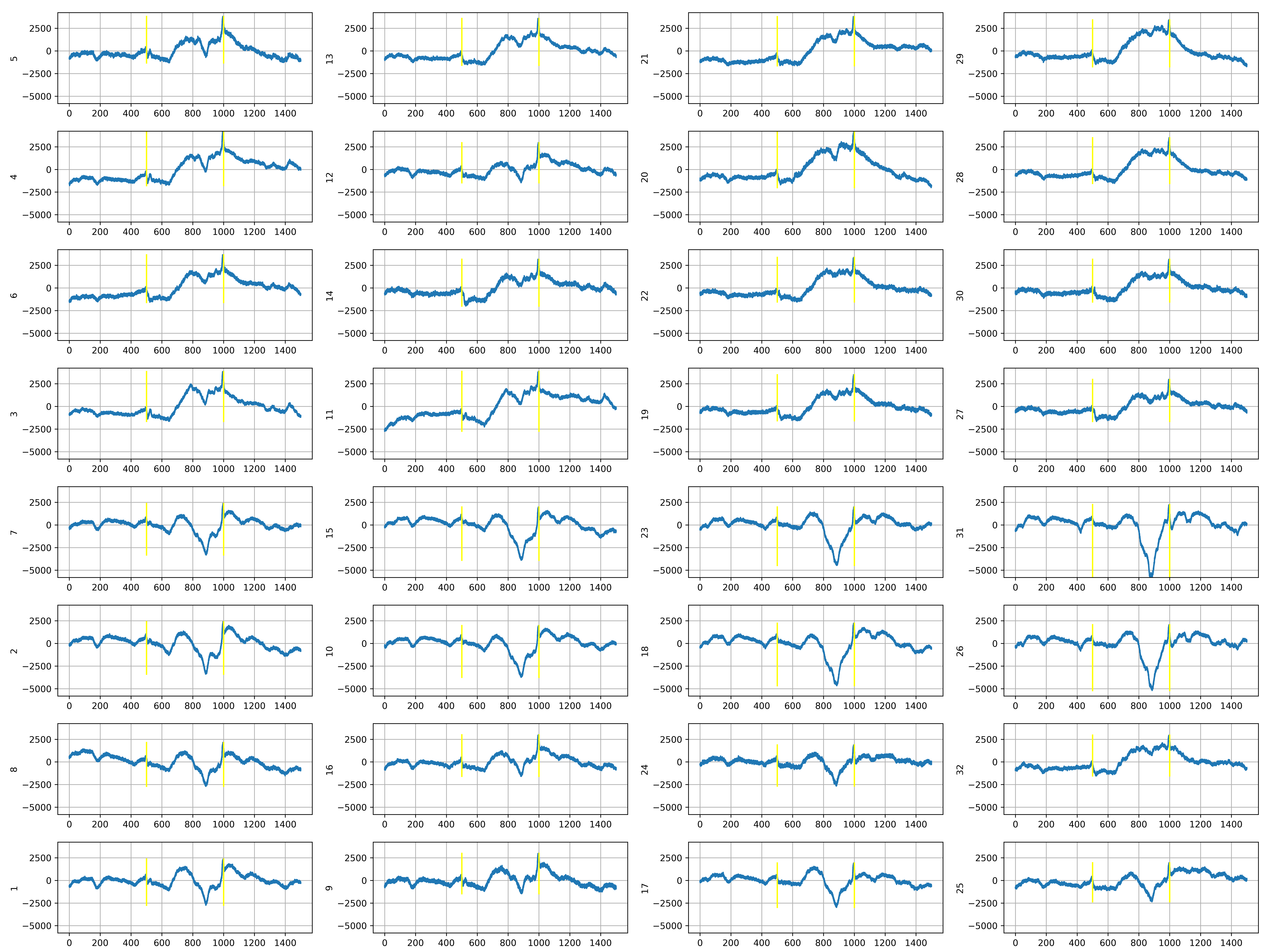
Raw average of Ab (V1) ¶
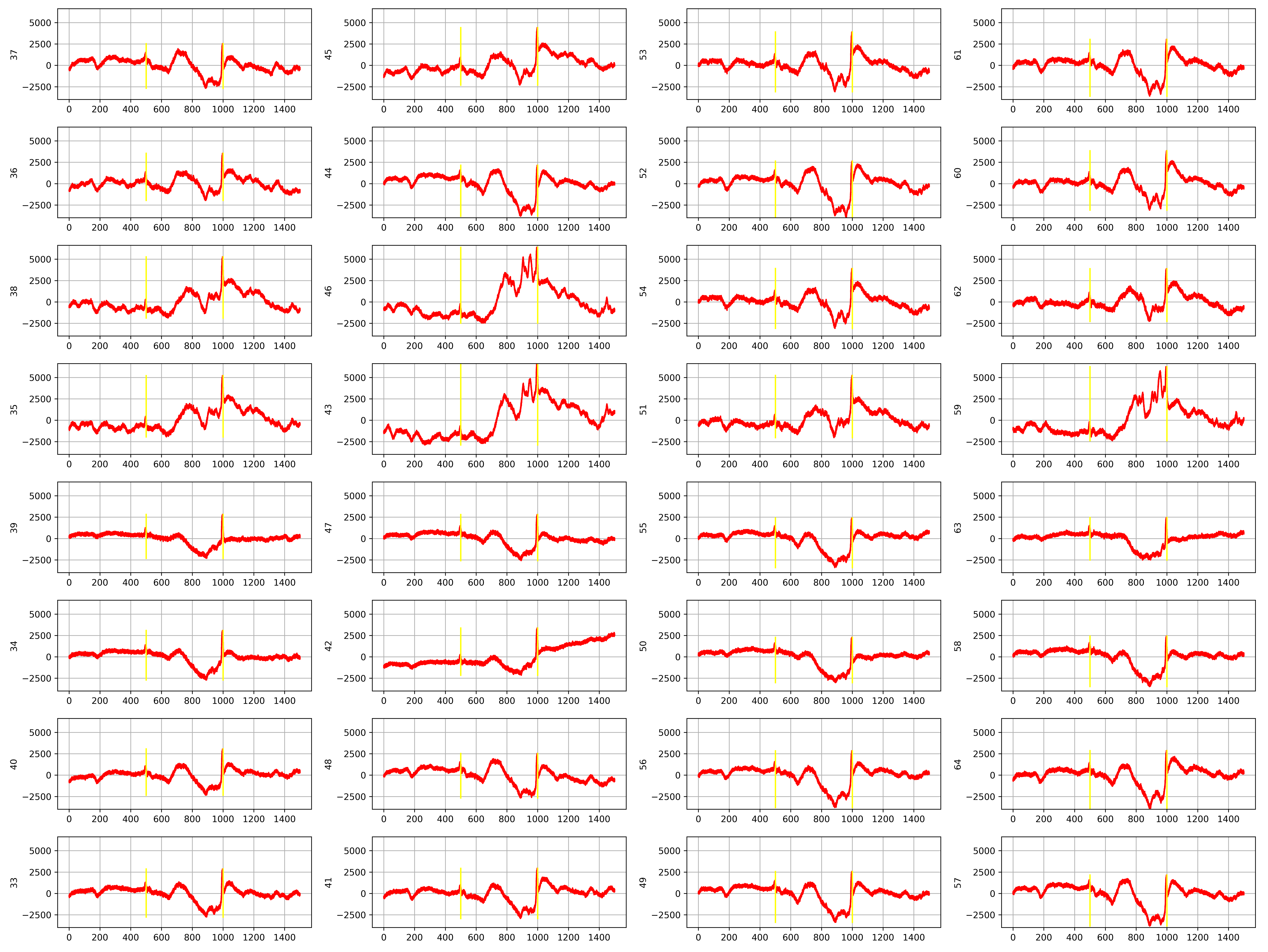
Raw average of Ab (AL) ¶
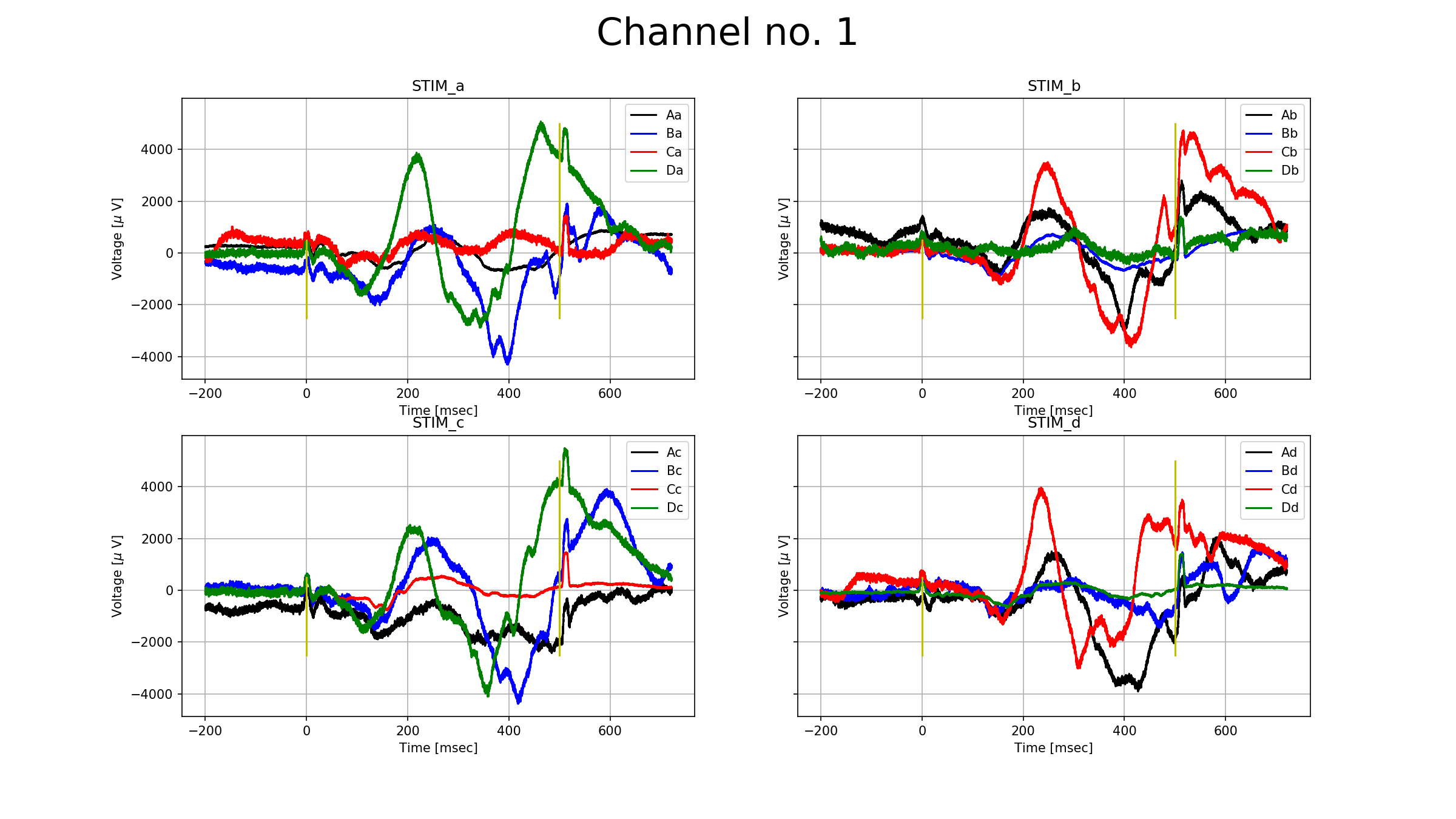
Comparison of responses (ch1 from V1) ¶
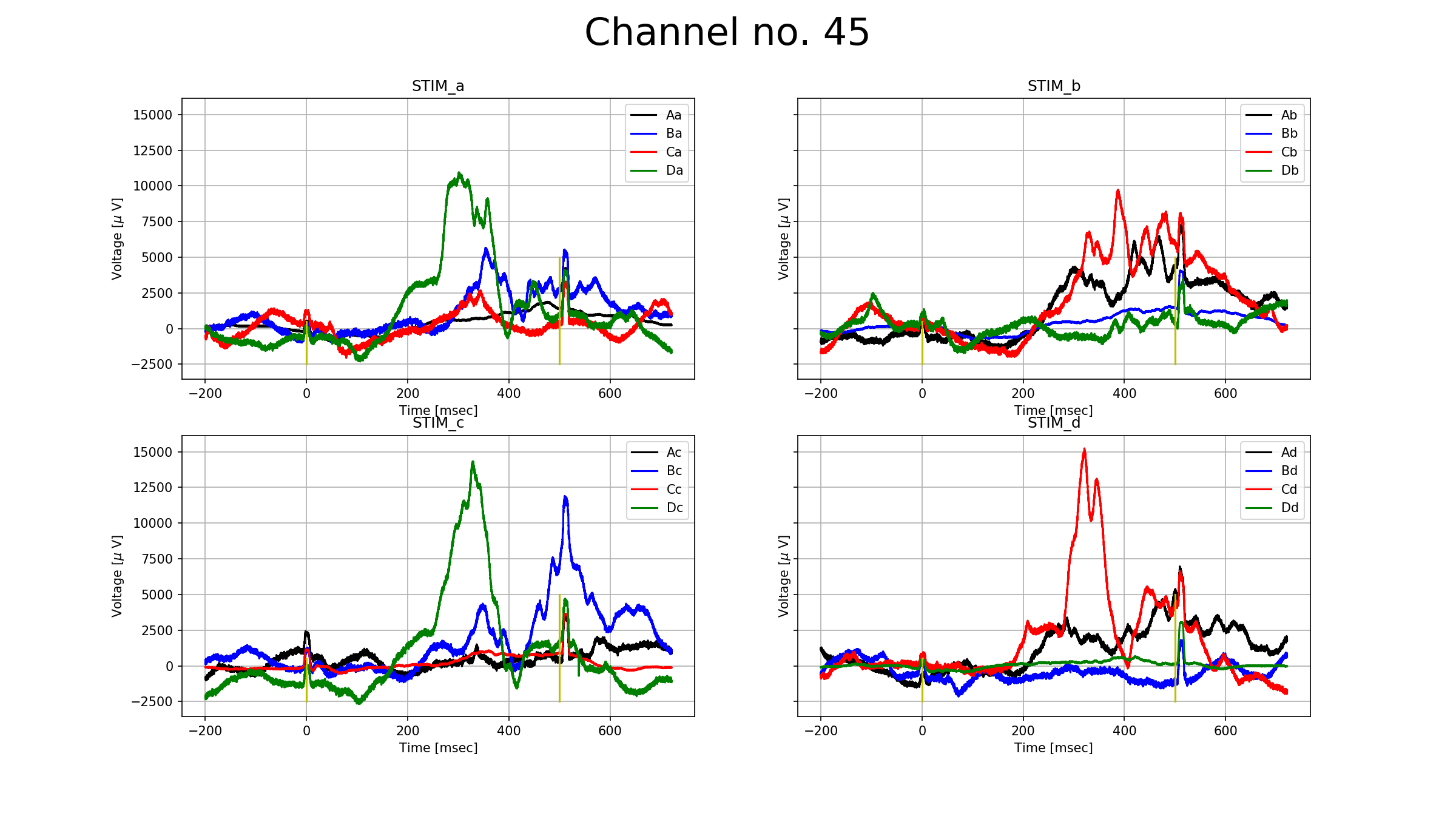
Comparison of responses (ch45 from AL) ¶
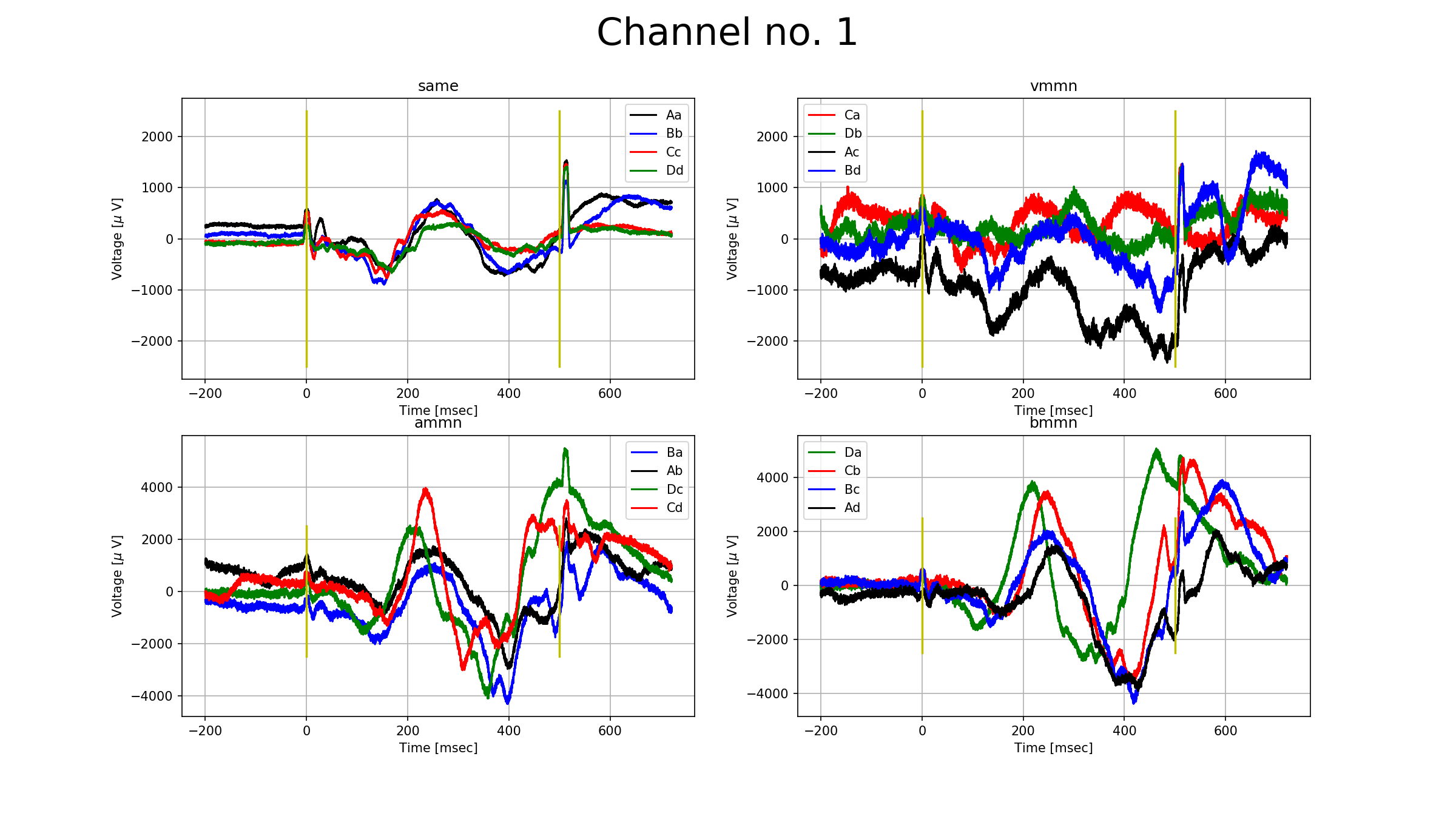
MMN types (ch1 from V1) ¶
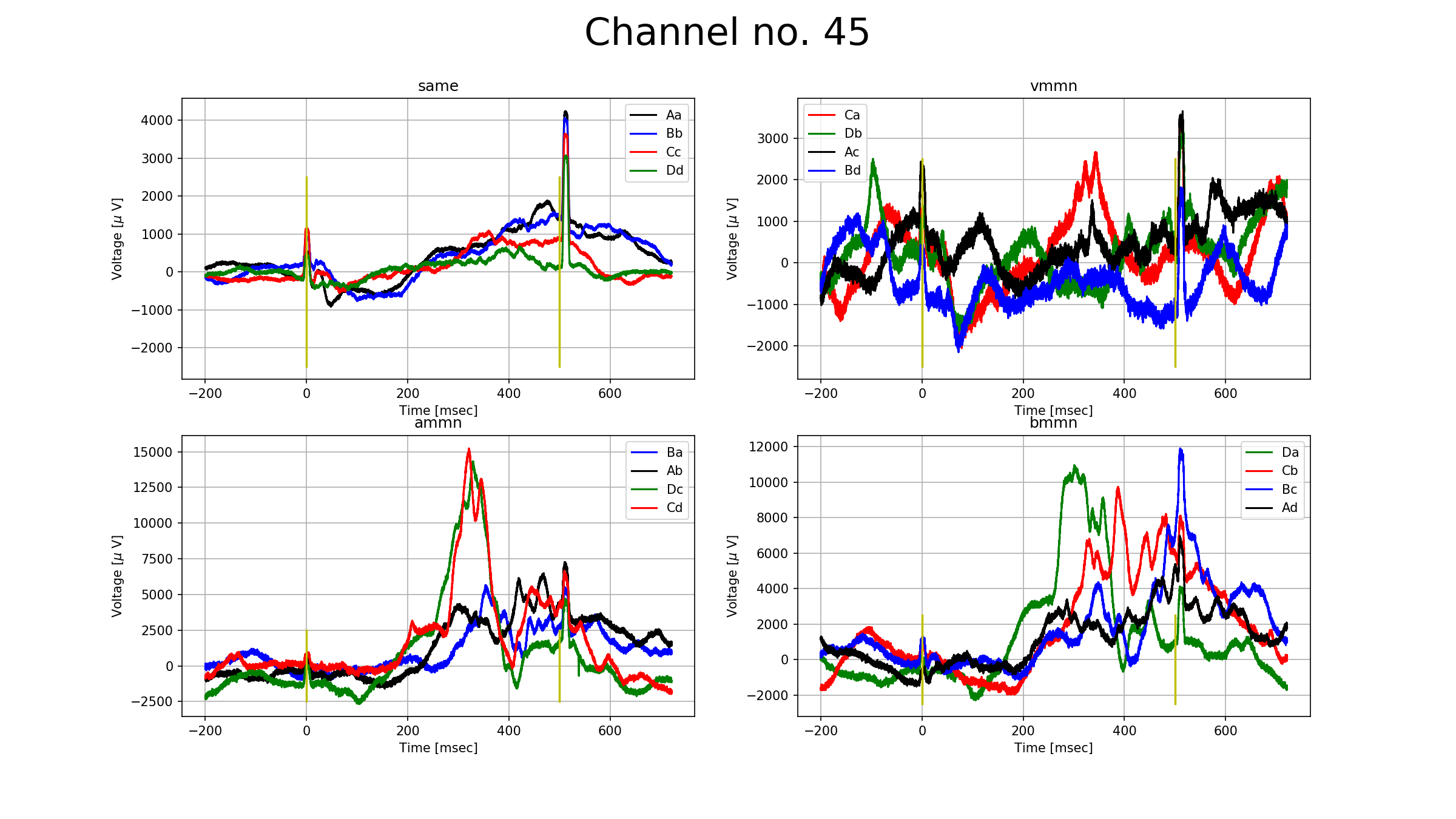
MMN types (ch45 from AL) ¶
Sidenote ¶
Coherency ¶
The cross-spectrum $(S_{xy})$ of two temporal signals $(x,y)$ is the following : $$ \left< S_{xy} \left( f \right) \right> = \frac{2\Delta^2}{T} \frac{1}{K} \sum_{k=1}^K F_x^k \left(f\right) F_y^{k,*}\left(f\right), $$
where
- $\Delta$ : timestep ($dt$)
- $T$: length of a trial
- $K$ : trials
- $F_x^k$: Fourier spectrum
and the coherency:
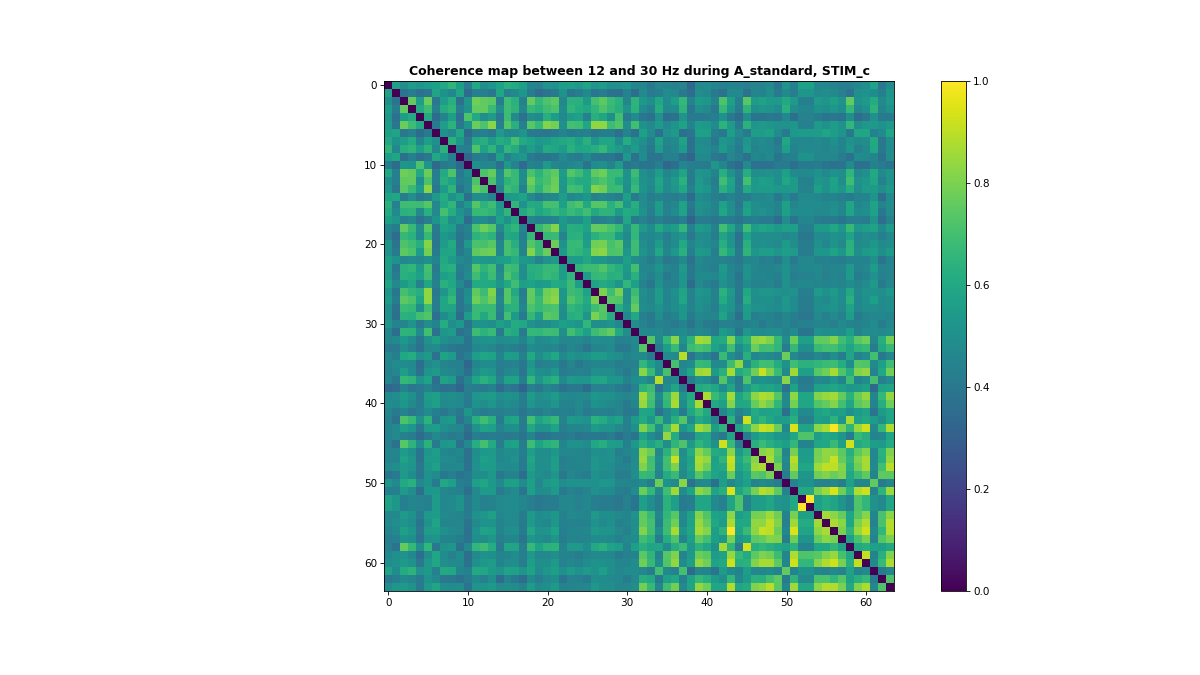
$$ \kappa_{xy} \left( f\right) = \frac{\left| \left< S_{xy}\left(f\right) \right> \right|}{\sqrt{\left< S_{xx}\left(f\right)\right>\left< S_{yy}\left(f\right)\right>}}. $$ Total coherency map ¶
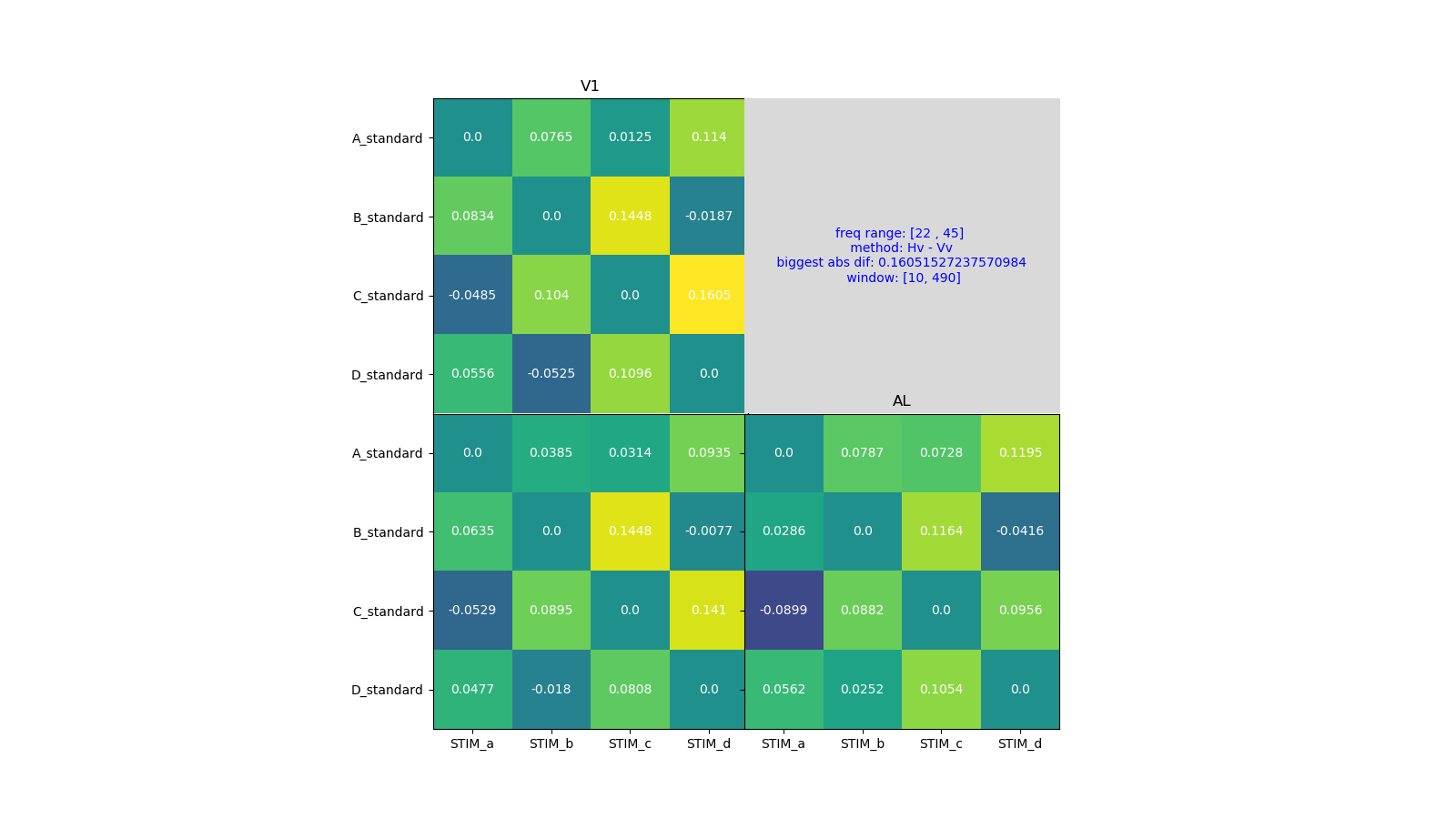
Coherency-difference averaged map ¶
Coherency-difference MMN map of V1 ¶
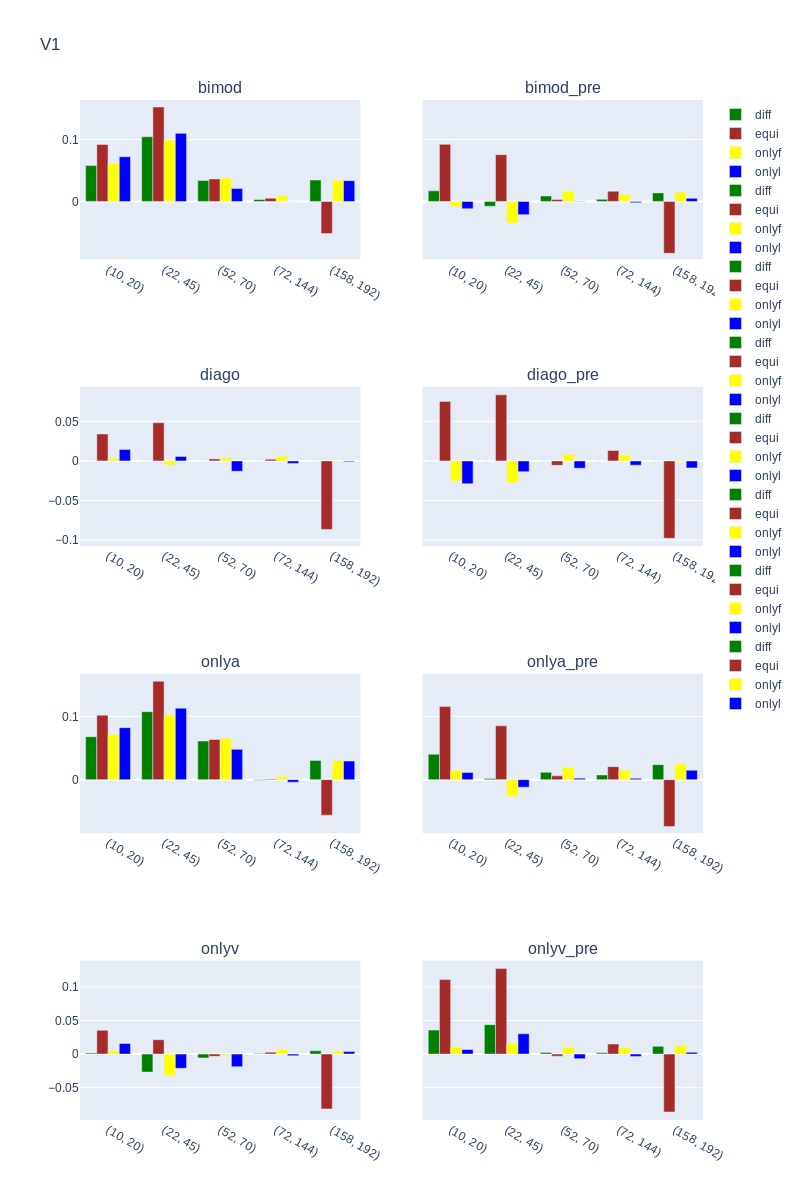
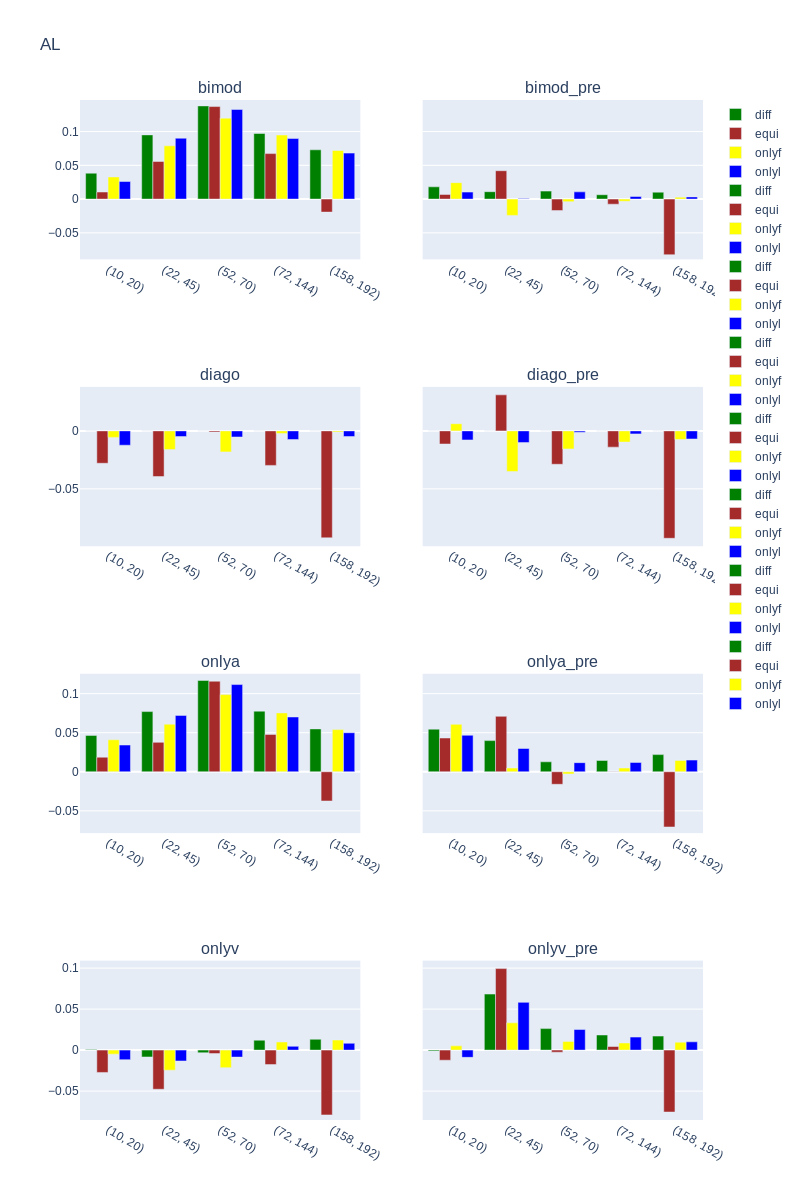
Coherency-difference MMN map of AL ¶
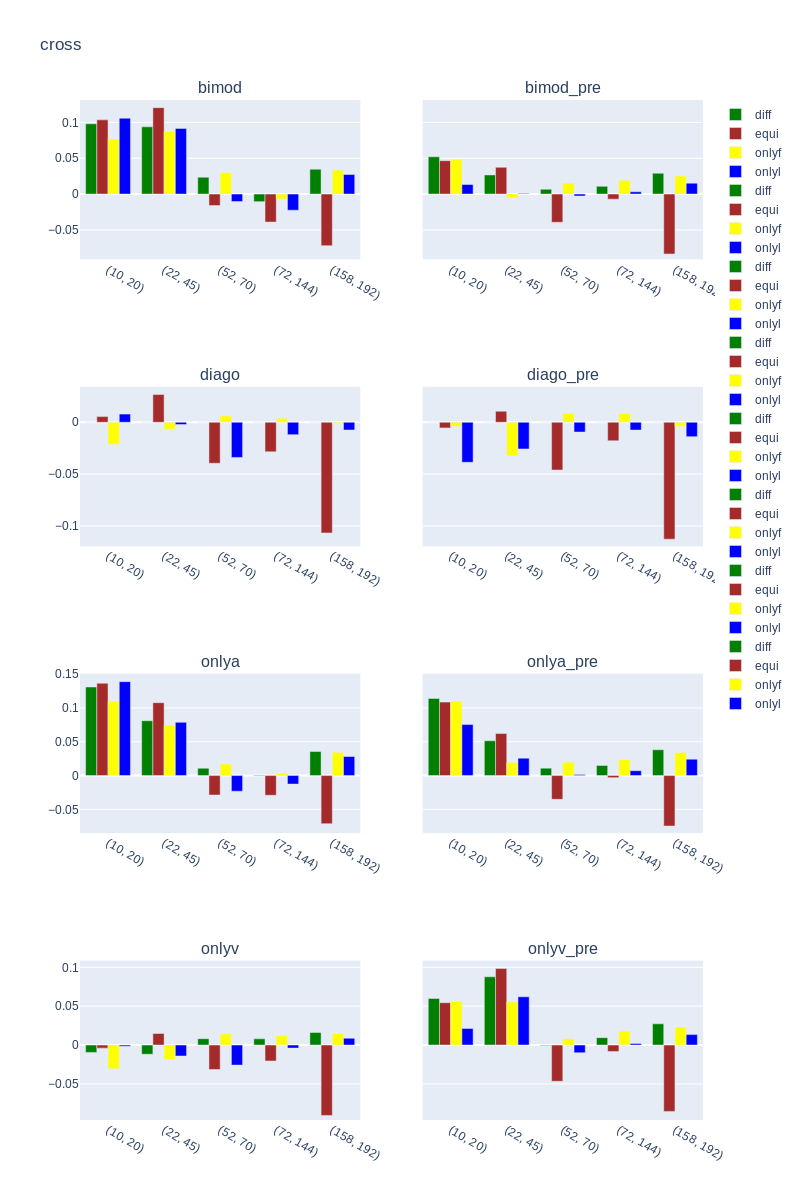
Crosss-coherency-difference MMN map of V1 and AL ¶
#TODO ¶
- Group by other paramteres (freq, mmn, type, region)
- Significance test
- Compare to Fourier spectrum
- Do for all possible experiments
Our group ¶
- Zsigmond Benkő: MTA junior researcher, Phd candidate
- László Négyessy: Senior Research Fellow
Zoltán Somogyvári: Senior Research Fellow



References
- Iyer, Parameswaran Mahadeva, et al. "Mismatch negativity as an indicator of cognitive sub-domain dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis." Frontiers in neurology 8 (2017): 395.
- Näätänen, Risto, et al. "The mismatch negativity (MMN) in basic research of central auditory processing: a review." Clinical neurophysiology 118.12 (2007): 2544-2590.
- Amado, Catarina, and Gyula Kovács. "Does surprise enhancement or repetition suppression explain visual mismatch negativity?." European Journal of Neuroscience 43.12 (2016): 1590-1600.
- Epstein, Russell A., Whitney E. Parker, and Alana M. Feiler. "Two kinds of fMRI repetition suppression? Evidence for dissociable neural mechanisms." Journal of Neurophysiology 99.6 (2008): 2877-2886.
- Arnal, Luc H., and Anne-Lise Giraud. "Cortical oscillations and sensory predictions." Trends in cognitive sciences 16.7 (2012): 390-398.
- Bastos, Andre M., et al. "Canonical microcircuits for predictive coding." Neuron 76.4 (2012): 695-711.
- https://www.myndlift.com/single-post/2018/01/23/How-Does-Our-Brain-Work-1
In [ ]: